
1The concept of functional safety
What is functional safety? Functional safety is an integral part of overall safety related to EUC or EUC control systems, which depends on electrical safety
The correct functioning of gas/electronic/programmable electronic (E/E/PE) safety systems, other technical safety systems, and external risk reduction facilities
Make it.
How to exercise correctly? The main content includes two aspects: management and technology. Ensure that the E/E/PE safety system, other technical safety systems, and external risk reduction facilities can perform safety functions when needed, both technically and administratively.
In process industries such as petrochemicals and chemicals, safety related systems are described using safety instrumented systems. SIS (Safty Instrumented Systems) is an instrument system used to implement one or several instrument safety functions, which can be composed of any combination of sensors, logic solvers, and terminal components
A Safty Instrumented Function is a safety function with a specific SIL to achieve functional safety. It can be either a safety protection system or a safety control system
2、 SIS overall safety lifecycle
The overall safety lifecycle of an SIS includes concepts, overall scope definition, hazard and risk analysis, overall safety requirements, safety requirement allocation, overall safety plan development (operation and maintenance plan, overall safety confirmation plan, overall installation and commissioning plan), implementation of E/E/PES safety related systems, implementation of other safety related systems, implementation of external hazard reduction facilities, overall installation and commissioning, overall safety confirmation, overall operation maintenance and repair, overall modification and retrofitting, shutdown and disposal.
Each stage of the overall safety lifecycle has its own related functional safety activities and requirements. The implementation of E/E/PES safety related systems includes two parts: hardware implementation and software implementation. This stage is designed to meet the SIL requirements of the system. So, we say that functional safety is designed.
The implementation phase of E/E/PES safety related systems includes safety requirement specifications (safety function requirement specifications and safety integrity requirement specifications), safety confirmation plans, design and development, integration, operation and maintenance procedures, and safety confirmation (IEC61508-2).
The software security lifecycle (implementation phase) includes: software security requirements specification (security function requirements specification and security integrity requirements specification), software security confirmation plan, software design and development, PE integration (hardware and software), software operation and maintenance procedures, and software security confirmation (IEC61508-3).
3Assessment of functional safety
The purpose of functional safety assessment is to investigate and assess the functional safety achieved by E/E/PE safety related systems. The functional safety assessment of SIS is conducted from two aspects. Firstly, evaluate whether the management activities necessary to ensure functional safety objectives are effective. Secondly, evaluate whether the safety instrumented system or safety instrumented system meets the required SIL. How to confirm that the SIL of safety instruments and SIS in design and production meets the requirements? We can consider the following aspects:
(1) Establish a functional safety management system
The purpose of establishing a functional safety management system is to determine the management and technical activities of all stages of the overall, E/E/PES, and software safety lifecycle, which are necessary to achieve the functional safety requirements of E/E/PE safety related systems; Determine the responsibilities of personnel, departments, and organizations for each stage or activity within the overall, E/E/PES, and software security lifecycle. Ensure the required safety and integrity through the system.
(2) Establish documents related to functional safety
The document should specify the necessary information for effectively executing the overall safety lifecycle, E/E/PES safety lifecycle, and software safety lifecycle stages; Provide the necessary information to effectively carry out activities such as functional safety management, verification, and functional safety assessment; In order to meet the requirements of IEC61508 for documentation, relevant documents must be provided for each activity in each stage of the overall safety lifecycle during the reporting and recording of functional safety assessments. Examples of documents required for functional safety assessment can be found in Appendix A of IEC61508.1.
(3) Determination of Safety Integrity and Safety Integrity Level
Safety integrity refers to the average probability of successfully achieving the required instrument safety functions under specified conditions and within a specified time.
The safety integrity level is a separation level used to specify the safety integrity requirements assigned to SIS safety functions, denoted as SIL, which is divided into four levels, with SIL4 being the highest level. IEC61508-1 specifies the target failure quantity (Table 1).
When determining safety integrity, all failure factors (hardware random failures and system failures) that cause non safety states should be included.
The usage mode of safety related systems can be divided into low demand mode (≤ 1 time/year) and high demand or continuous mode (>1 time/year) according to the required frequency. The target failure levels for SIL in low demand mode and high demand mode are different, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Safety Integrity Level: Target Failure Levels for SIL in Low and High Requirement Modes

(4) Evaluation of Software and Hardware SIL
① Requirements for hardware fault margin
Hardware failure margin refers to the ability of a component or subsystem to continue performing the required instrument safety functions in the event of one or several hardware failures. The hardware failure margin N means that N 1 failures will result in the loss of full functionality. For example, if the hardware failure margin is 1, it means that if there are two devices, their structure should be such that the dangerous failure of one of the two components cannot prevent the occurrence of safety actions. In order to mitigate potential defects in the design of instrument safety functions, Tables 5 and 6 of IEC61511-1 define the minimum hardware margin for sensors, logic solvers, and terminal components. For instrument safety functions, sensors, logic solvers, and final components should have the lowest hardware fault margin, which represents the lowest component or subsystem redundancy.
② Structural constraints on hardware security integrity
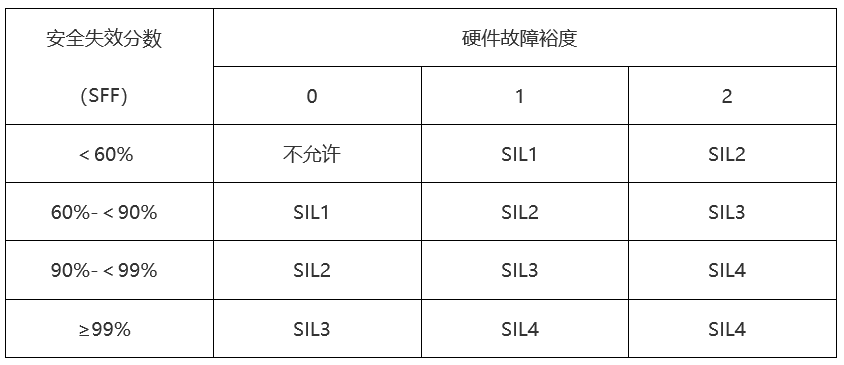
The maximum safety integrity level declared by hardware security functions is limited by the hardware failure margin and the safety failure score (SFF) of the subsystems that perform the security function. Tables 2 and 3 in IEC61508.2 are for Class A and BStructural constraints of class related subsystems, representingThe relationship between SIL and the minimum hardware fault margin when the failure fraction (SFF) is determined.
When conducting SIL assessment, we first need to distinguish whether the hardware structural constraints belong to Class A or Class B based on whether the failure modes of the components or subsystems are known, whether the data is reliable, and whether the fault behavior is determined.
Then, perform SFF and PFDCalculation, correspondingThe corresponding SIL can be obtained from Table 2 or Table 3 of IEC61508.1.Namely, components andThe security integrity level of the relevant subsystems.
When determining the maximum hardware safety integrity level of a subsystem, system structural constraints must be considered, that is, the correspondence between fault margin requirements and SIL under the premise of SFF determination. Table 2 shows the structural constraints of Class B related subsystems.
Table 2 Safety Integrity Level: Structural Constraints of B-class Related Subsystems
7、 Conclusion of SIL certification
To meet the requirements of functional safety standards, it is necessary to demonstrate that all proposed requirements comply with the relevant functional safety standards
(such as safety integrity level) and has met the requirements of each chapter and article. However, for some systems and instruments that are reasonably considered unnecessary, the requirements of these clauses in the standard can be disregarded.
At the end of the functional safety assessment, there are only three conclusions, namely acceptance, conditional acceptance, or non acceptance.
8、 The Relationship between Functional Safety and EMC Environment
An E/E/PES safety related system may encounter electromagnetic interference during the execution of safety functions, which may result in errors, misoperations, malfunctions, and damage, leading to performance degradation or failure of the safety related system, and even causing danger. In the functional safety standards, special emphasis is placed on evaluating the EMC characteristics of E/E/PES safety related systems to ensure the required failure rate specified by SIL. At present, relevant international organizations are working on researching and formulating electromagnetic compatibility requirements for safety related systems (equipment), which has led to the formation of
IEC61326-3 (draft). IEC61326-3 (draft) specifies additional requirements for the immunity level of safety related system equipment. Moreover, the EMC performance criteria for safety related systems (devices) are different from the performance criteria defined by general standards and IEC61326-1.
Therefore, during certification, the product must comply with electromagnetic compatibility requirements related to functional safety.
9、 Conclusion
① Safety is the eternal theme of industrial production. Therefore, carrying out SIL certification to ensure the safe use of domestic instruments and systems in various application fields plays a positive role in improving the core competitiveness of domestic instruments and systems in the market.
② Through SIL certification, domestic SIS users, design departments, integrators, equipment manufacturers, and suppliers can recognize and understand the concept of functional safety, and correctly apply relevant standards to achieve the required safety functions. By effectively managing and evaluating functional safety to meet relevant security standards and contractual requirements, we aim to enhance our competitiveness.
③ EMC of safety related systems (equipment)Requirements andThe EMC performance criteria are higher than those for non safety related systems; Safety related systems (equipment), their SILThe higher the level, the higher the EMCThe higher the requirements.
Service Hotline: 18924609560 (same WeChat account)

|
||||||
|
||||||